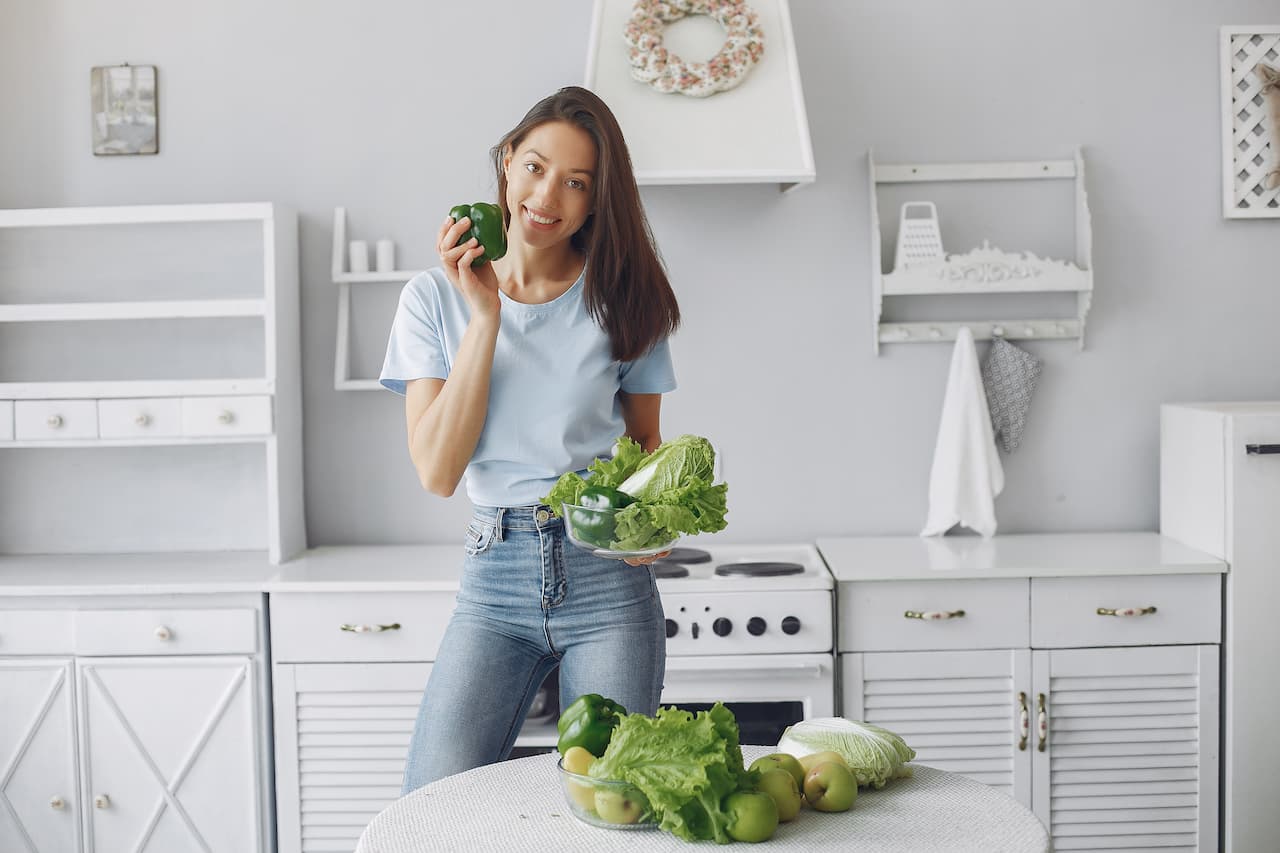
Understanding the basics of a balanced diet
A balanced diet is essential for maintaining good health and well-being. It provides the body with necessary nutrients to function correctly. The basic principle of a balanced diet involves consuming the right proportions of different food groups: carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and water. Carbohydrates are the body’s primary energy source, and they should mainly come from whole grains, fruits, and vegetables rather than sugary snacks and processed foods.
Proteins are vital for growth and repair of tissues. They can be sourced from both animal products, such as meat, fish, and eggs, and plant-based foods like beans, lentils, and nuts. Including a variety of protein sources ensures that one receives all essential amino acids. Fats, though often vilified, are crucial for the absorption of vitamins and the production of hormones. Healthy fats can be found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and oily fish, while saturated fats and trans fats should be limited.
Vitamins and minerals are required in smaller amounts but are vital for maintaining immune function, bone health, and overall metabolism. A colorful plate typically ensures a range of these micronutrients. Lastly, water is indispensable for digestion, nutrient transport, and temperature regulation. Adults should aim to drink at least eight glasses of water daily, though individual needs may vary based on activity level and climate.
The benefits of eating seasonal and local produce
Eating seasonal and local produce is a significant component of a healthy lifestyle. Seasonal fruits and vegetables are at their peak in terms of flavor and nutritional content. They are typically harvested at the right time, allowing them to develop their full range of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. For instance, strawberries picked in season are more nutrient-dense compared to those grown out of season in greenhouses or imported from afar.
Local produce also offers the benefit of reduced environmental impact. Transporting food over long distances contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, and by choosing locally grown food, one can help minimize this environmental footprint. Additionally, supporting local farmers and markets boosts the local economy and promotes a sense of community.
Moreover, local produce tends to be fresher. Often, it is harvested shortly before being sold, which means fewer nutrients are lost during transport and storage. Fresh produce not only tastes better but also provides greater health benefits. Shopping at farmers’ markets or joining a local food co-op can be a delightful experience, offering a direct connection to the people who grow the food and insights into their farming practices.
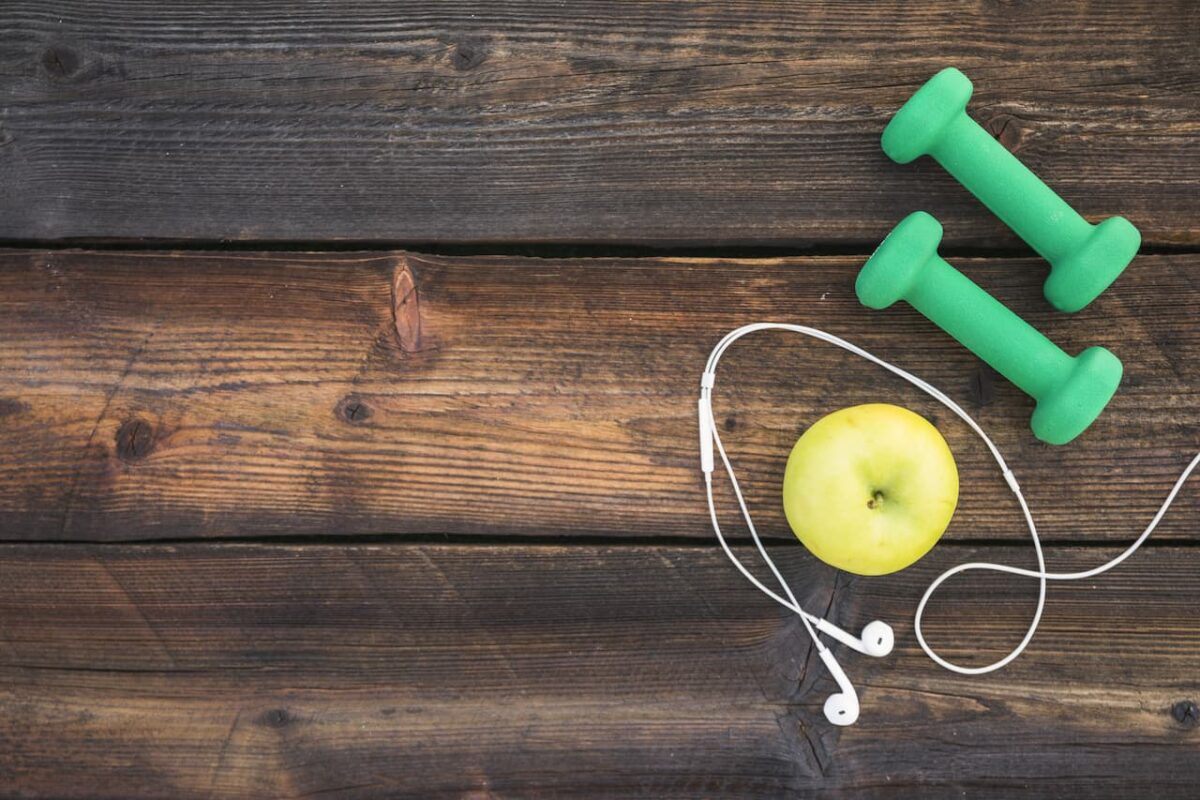

Practical tips for maintaining a healthy diet
Maintaining a healthy diet can be challenging amidst busy lifestyles and the prevalence of convenience foods. However, with some practical tips, it is possible to make healthier choices easier. Planning meals ahead of time is one effective strategy. Meal planning reduces the likelihood of resorting to unhealthy fast food or ready-made meals. It also ensures that a variety of food groups are included in each meal.
Incorporating more whole foods into the diet is another crucial step. Whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, are minimally processed and packed with essential nutrients. On the other hand, highly processed foods often contain added sugars, unhealthy fats, and artificial ingredients, which can contribute to various health issues.
Portion control is also vital. Eating large portions, even of healthy foods, can lead to weight gain. Using smaller plates, serving sizes, and mindful eating practices, such as eating slowly and savoring each bite, can help regulate portion sizes. Listening to one’s body and eating when truly hungry rather than out of boredom or habit is a practice worth cultivating.
Lastly, staying hydrated is an often overlooked aspect of a healthy diet. Drinking water throughout the day helps to maintain energy levels, supports digestion, and can prevent overeating, as thirst is sometimes mistaken for hunger. Herbal teas and water-rich foods like cucumbers and watermelons can also contribute to hydration.
By understanding the fundamentals of a balanced diet, embracing seasonal and local produce, and incorporating practical dietary habits, one can significantly enhance their overall health and well-being. Adopting these practices not only contributes to physical health but also supports environmental sustainability and community well-being